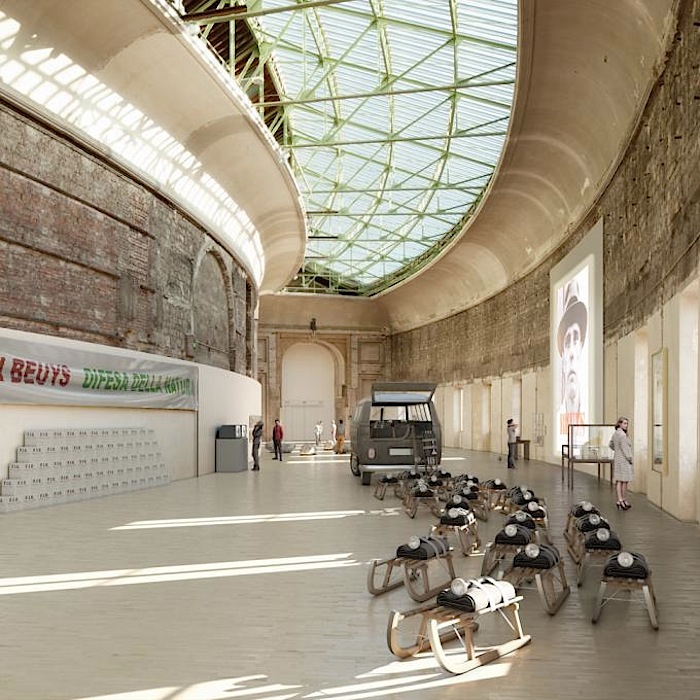
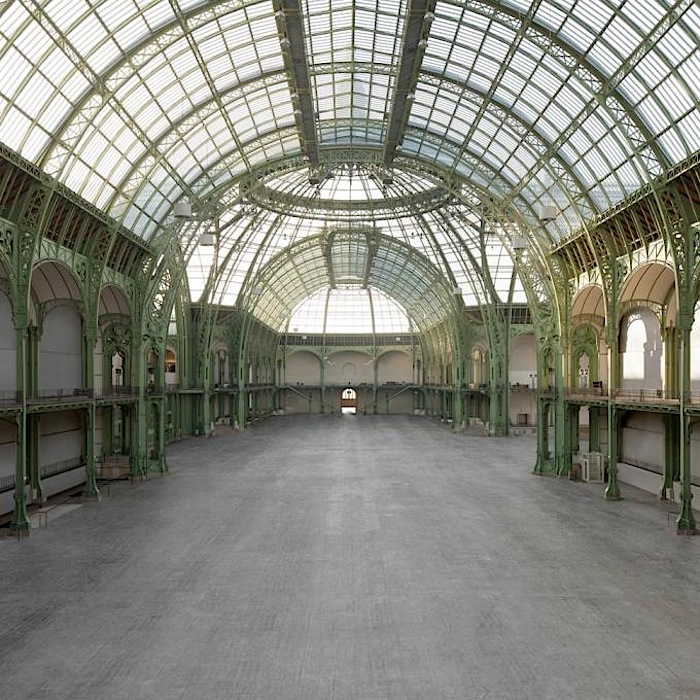
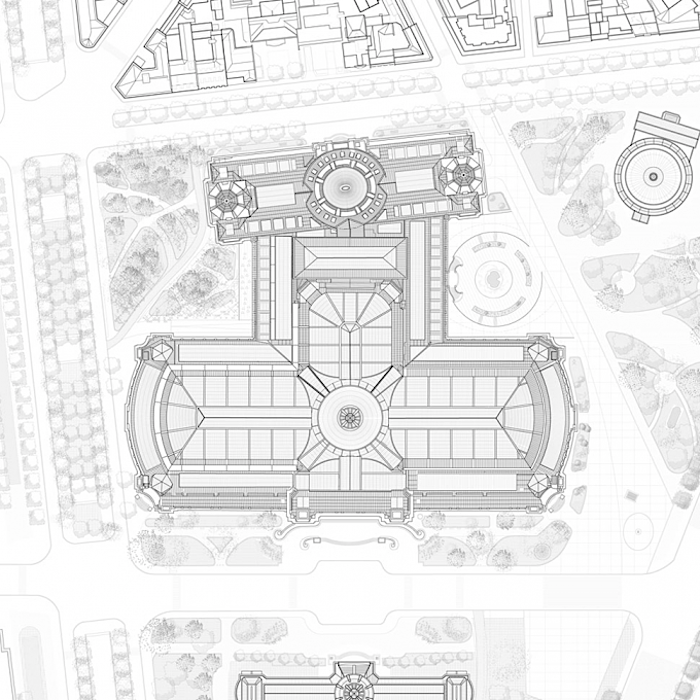
El concurso del Grand Palais de Paris tiene ya ganador, y ha sido el joven equipo LAN (Local Architecture Network) formado por Benoit Jallon y Umberto Napolitano.
Con un presupuesto de 130 millones de euros el palacio parisino de mas de 70 mil metros cuadrados, que se construyó para la feria mundial de 1900, se convertirá en un nuevo hito en el paisaje cultural internacional.

Para ver el reportaje completo de renders y plantas mira el sigue leyendo….
Memoria del proyecto:
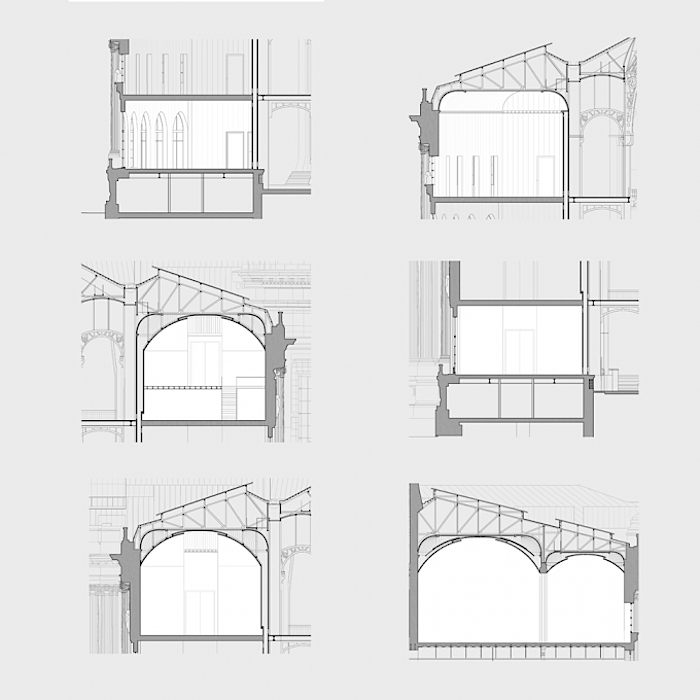
To our contemporary eyes, the Grand Palais is both an idea and a symbol of modernity. It is a hybrid building in terms of its architecture, its usage and its history. Neither a museum nor a simple monument, its architecture has an identity all its own, centred around the notion of a «culture machine», a spatial means for hosting a vast diversity of events and audiences that exponentially exalts the site’s «universal» and «republican» vocation. The restoration and restructuring of the entire monument affords us the chance to reinforce this aspiration.
The coming restructuring foresees the implementation of a new circulation mechanism centred around the middle building, the restoration of the galleries surrounding the Grand Nave, the installation of a climate control system, the creation of a logistics centre, bringing the entire building up to code, and opening the large bay windows and passageways in order to restore the building’s original coherence and sense of transparency. These interventions represent a unique opportunity to re-discover the traces and ways in which the Grand Palais has withstood the test of time, survived changes in its function, to assert architecture as a point of departure, and the space as nurturing life and society.
Even though the initial reason for building the Grand Palais was to provide a site for presenting and promoting French artistic culture during the World’s Fair of 1900, the plan nevertheless envisioned durability and flexibility from the outset. Even though these many adaptations progressively complicated and depreciated certain parts of the Grand Palais, the intelligence of its general form and its original spatial intent have helped it survive these episodes and change with the times.
Our credo for the New Grand Palais is to complete and strengthen its formal logic through interventions that return a sense of modernity to its whole, all the while respecting its traditional identity.
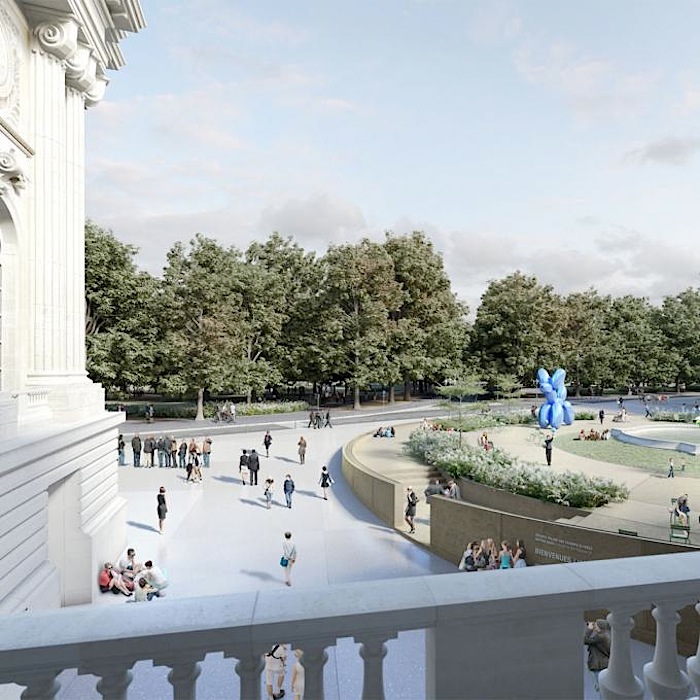
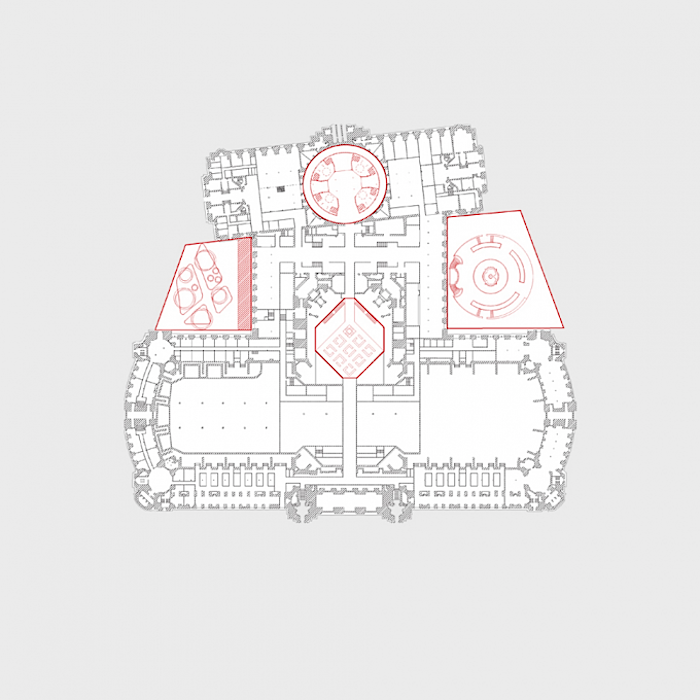
The Jean Perrin Square and the ‘Jardin de la Reine’
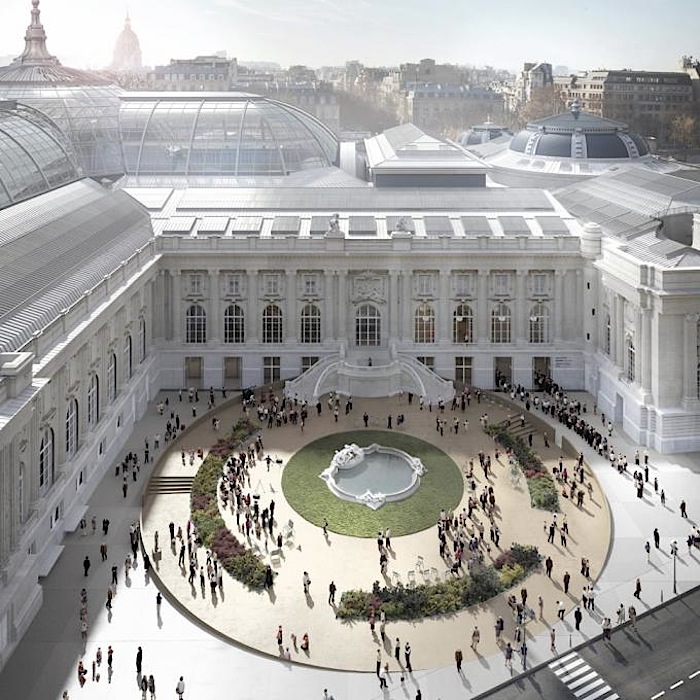
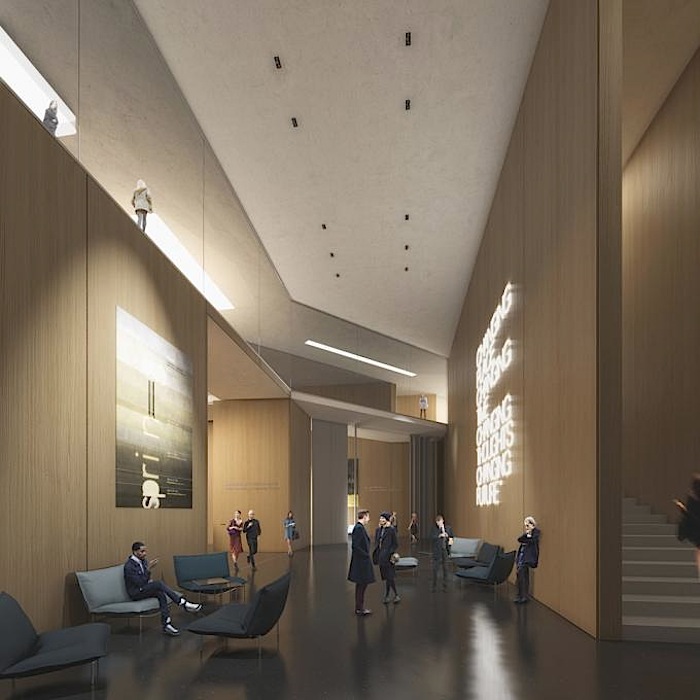
The logical consequence of revamping the northern and southern access points, one of the challenges of the project, is that the middle building lies at the heart of our intervention. Our wish is to reinforce the sense of unity between the Grand Palais and the Palais d’Antin and to make the middle building the meeting point between the two. This approach respects the architects’ original intentions, namely to render the spaces and their development highly legible to users, such that they implicitly signify the building’s function.
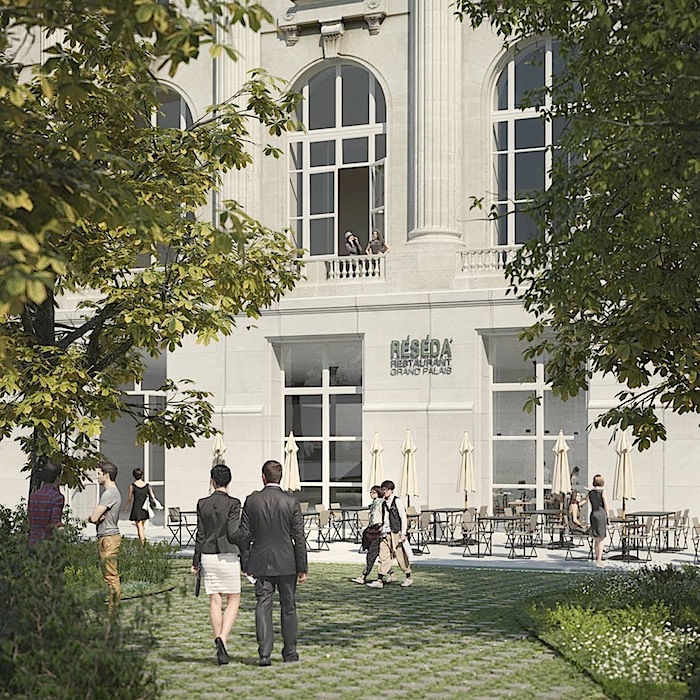
The pure geometry of the rediscovered circle creates a new symbol and marker at the urban level for the entrance to the New Grand Palais. It will become a veritable place of its own that can host planned or spontaneous activities. Two ramps, designed on the basis of the geometric matrix provided by the steps and the fountain, will lead visitors from the level of the square at the base of the building towards the entrance. Facing the Seine there will be the entrance for specific audience and the independent access to the restaurant. The latter takes advantage of a large terrace orientated to the south, located below the Jardin de la Reine.
The middle building: ‘La Grande Rue des Palais’
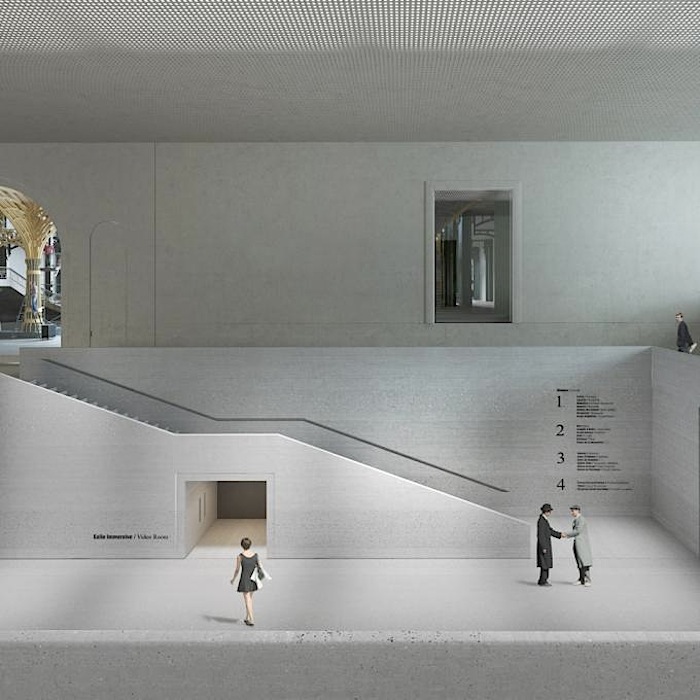
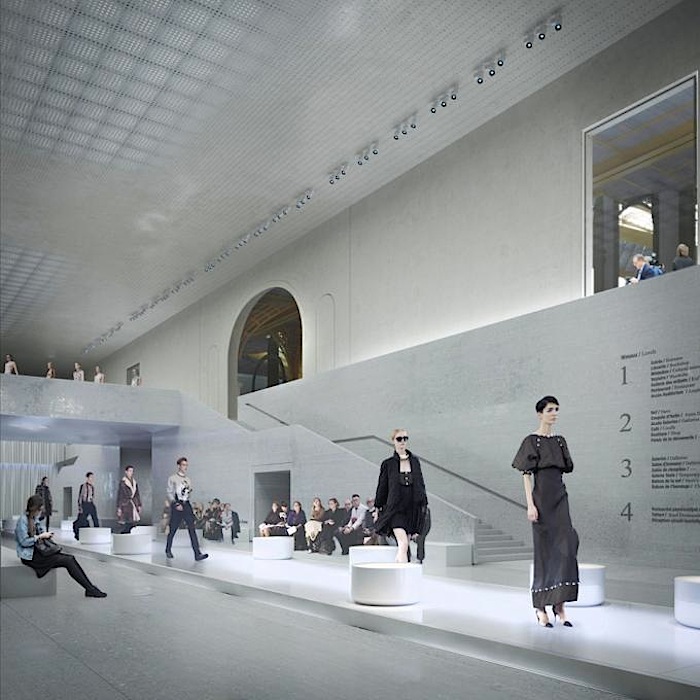
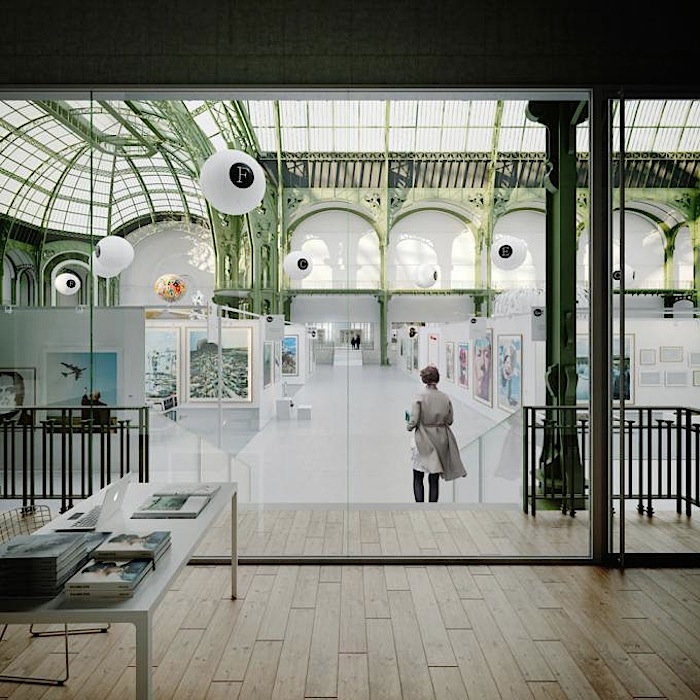
By creating a progressive transition from the urban space to that of the galleries, the first two floors of the middle building contain the ambulatory. It is a majestic, open volume with multiple levels that will allow the public to embrace the Grand Nave and the rotunda of the Palais d’Antin at the same time. In fact, it emphasizes the original east-west axis of the composition. Situated along the lower main level, ‘La Grande Rue des Palais’ organizes the different entrance phases in a clear sequence before leading the public to the various activities offered. The ambulatory will become the connecting platform for all exhibitions at the new Grand Palais. The materials chosen for la Grande Rue des Palais will link the exterior to the interior, the existing to the new. The dichotomy between the building’s foundation wall and the piano nobile, perceptible on the outside because of the change in stone colour, will continue inside the building.
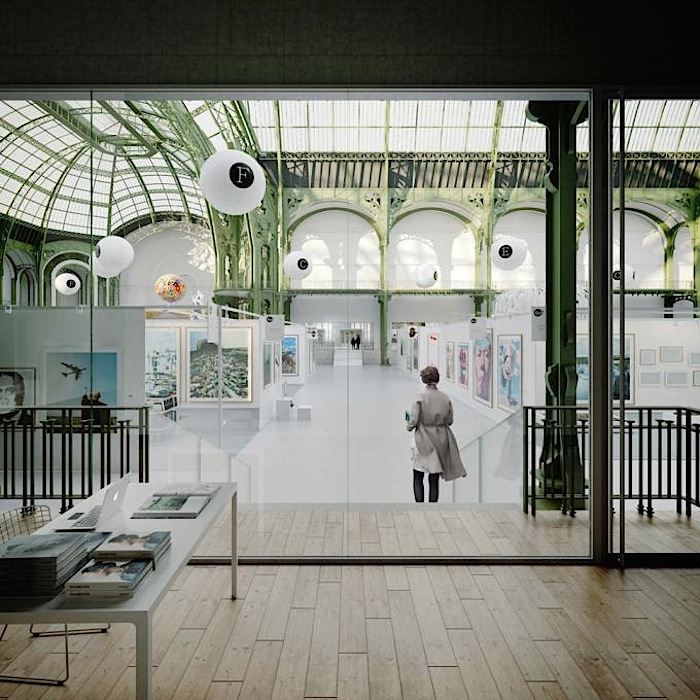
The exhibition spaces
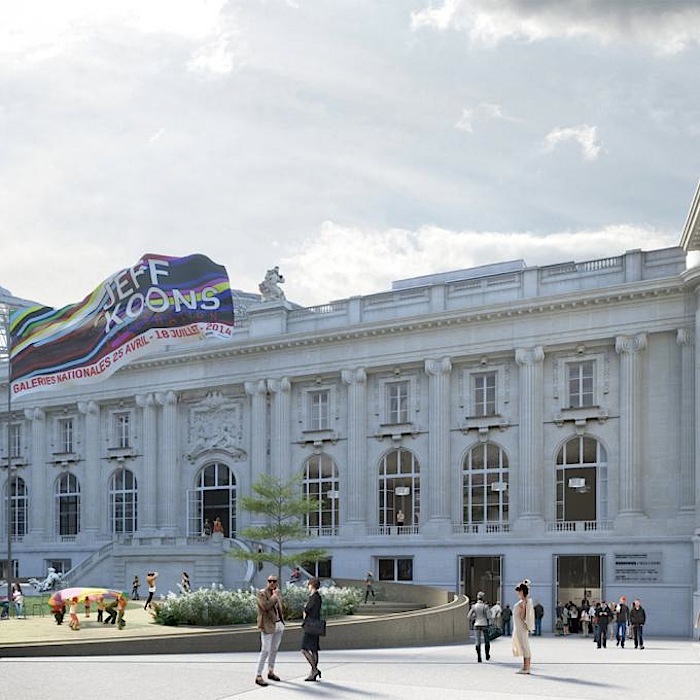
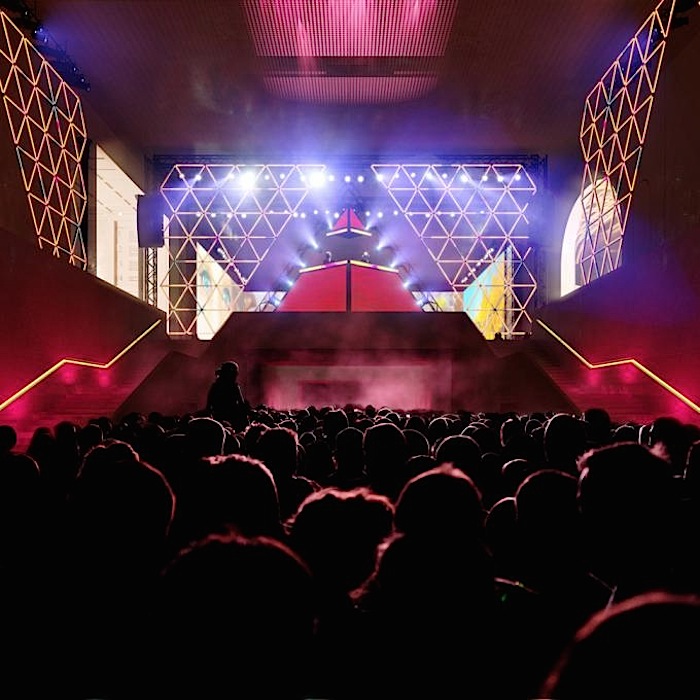
The restructuring of the National Galleries seeks to take into account the interdependence between comprehending a work and its formal and conceptual presentation. This becomes a unique opportunity to develop a vast range of diverse «situations» in terms of volumes, light, materials, and their relationship to the outside. It’s not simply a question of making the volumes flexible, but of giving them the ability to become an event in and of themselves. This process is not confined to the galleries; it can happen anywhere in the building, wherever the structure allows for it. By integrating innovative museographic concepts into the institution, the museum will be able to host works that, until now, have only been seen in alternative spaces for brief periods of time, and which have in fact not been commented on or valued enough.
The Grand Palais des Arts et des Sciences
The Palais de la Découverte will expose the public to other forms of culture, such as exhibitions, contemporary art, or high-quality live performances. Conversely, the public visiting the Grand Nave and the galleries will be exposed to new experiences upon visiting the Palais de la Découverte. The new temporary gallery in the Palais de la Découverte has been conceived with this in mind, as its central location concretises the link between these two realities.
The logistics platform and bringing up to code
For this project to become an effective way to hosting very diverse events and publics, it first of all demands a clear, flexible, and adaptable structuring of the spaces at hand. More than simply managing current needs, our proposal opens the door to the future evolutions of these needs. What is at stake is formulating a vision that in the long term can accept new parameters, evolutions in technology, and paradigm shifts.
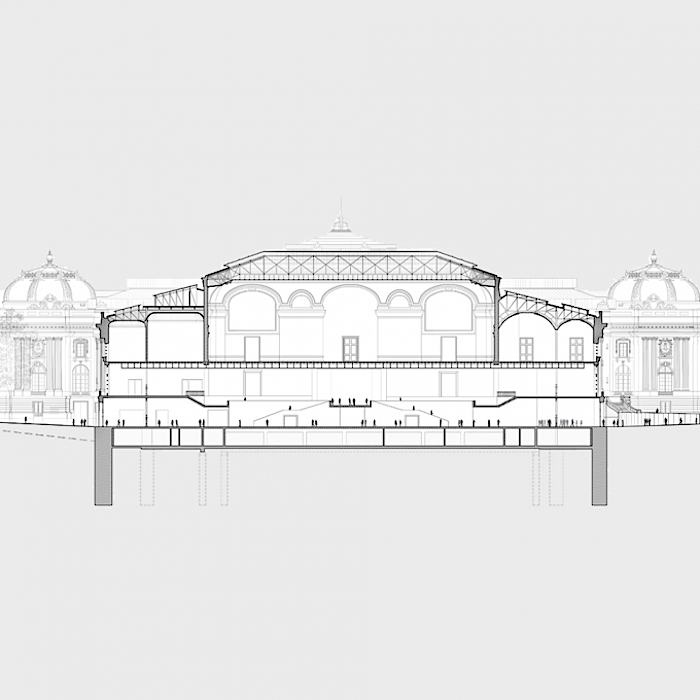
The program led us to create an underground level, which will host the logistics spaces and the associated parking and loading spaces. These technical works will permit an increase in visitor capacity to the Grand Palais. The Grand Nave will thus be able to accommodate more than 11,000 persons compared to the current 5,200, and this will increase its total visitor capacity from the current 16,500 to more than 21,900 persons.
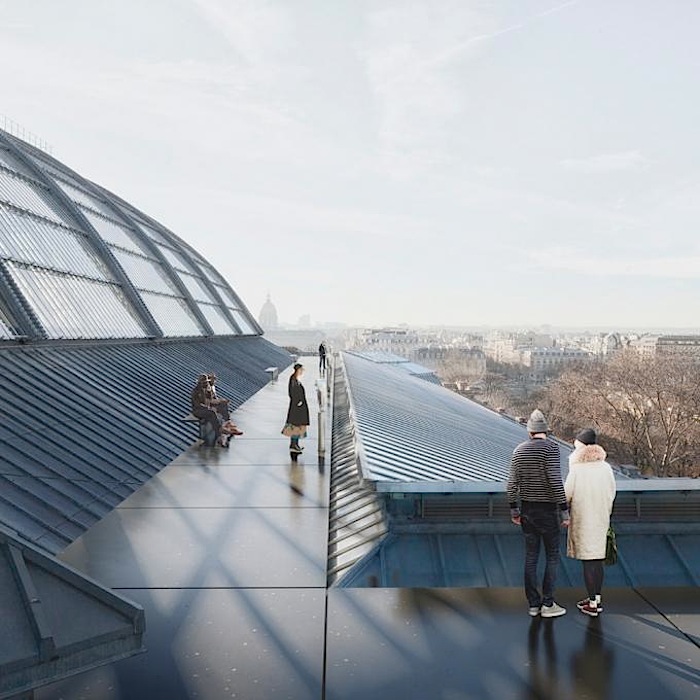
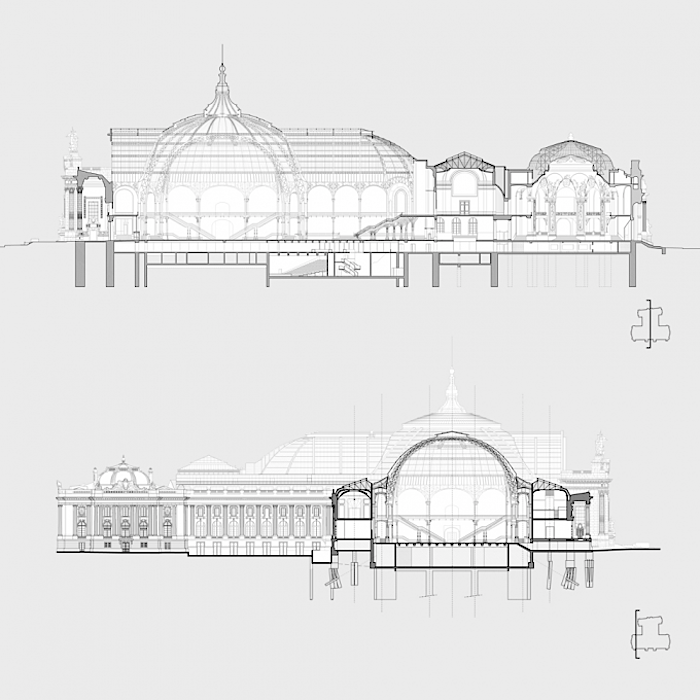
From the Grand Palais to the city – the flow of tourists and the observatory
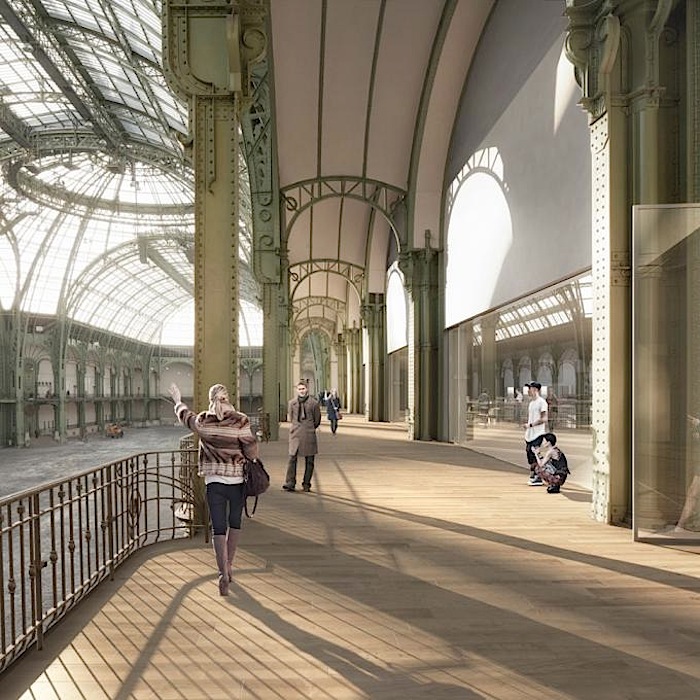
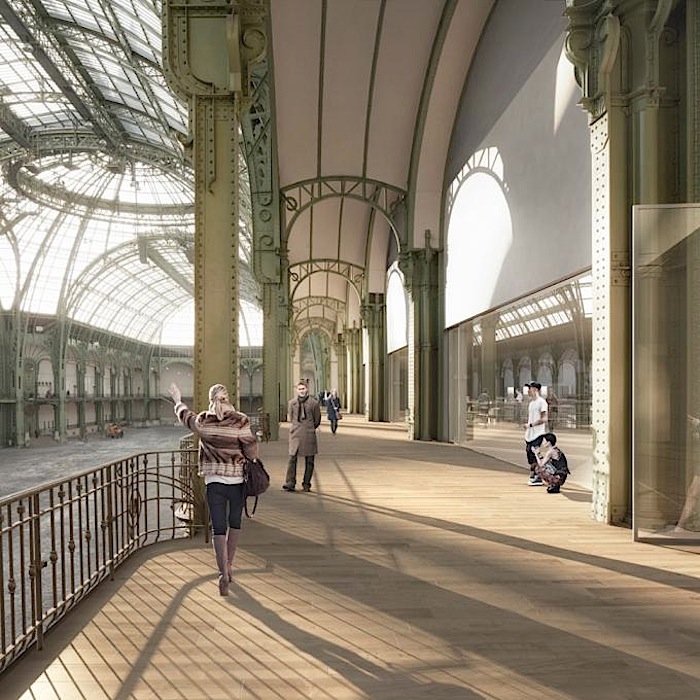
The movement of visitors within the Grand Palais represents an opportunity for «showing off» the architecture. By drawing the visitor’s attention, these views will frame «details» in the architecture and the landscape, thereby giving them emphasis. These views reveal themselves progressively as one walks through the space. They disclose the connection of the spaces that allow visitors to locate themselves within the building and in relation to the city. The internal tourist itinerary continues outside, along the rooftop of the Grand Palais, allowing visitors to discover the roof, and it will provide them with unobstructed, totally new vistas of Paris.
The monument to the dawn of sustainable development
We made use of a philosophy based on five main design values: Effectiveness, Sobriety, Strengthening Cultural Heritage, Minimal and Passive Intervention, and Remaining at the Service of Users. By analysing what is already there, the project is able to resolve and transform the challenges into strengths while at the same time identifying and preserving the quality of the inherited resources. Users (and future uses) have been placed at the heart of the design process by attempting to understand the many activities exercised and also by taking into account comfort and environmental requirements, be they climatic, acoustic, lighting-related, hygrothermic, and so forth. This intersection of situations, inherited resources, practices and activities, comfort and environmental requirements constitute the multi-faceted basis for this intervention. To reveal what is already there means to draw on the inherited resources to construct micro-contextual responses. One must in the end be hyper-contextual.